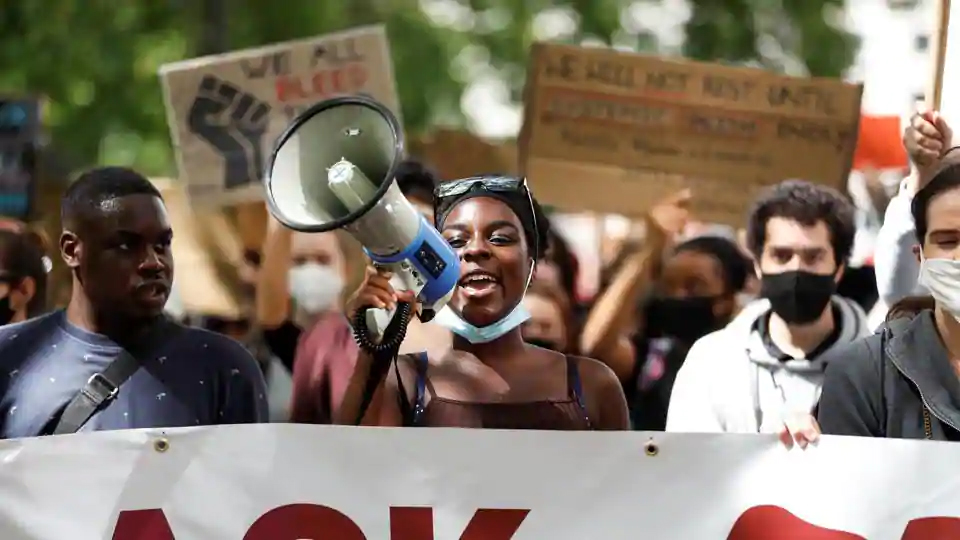A national coalition of labour unions, along with racial and social justice organizations, will stage a mass walkout from work this month, as part of an ongoing reckoning on systemic racism and police brutality in the US.
Dubbed the “Strike for Black Lives,” tens of thousands of fast food, ride-share, nursing home and airport workers in more than 25 cities are expected to walk off the job July 20 for about eight minutes — the amount of time prosecutors say a white Minneapolis police officer held his knee on the neck of George Floyd in May — in remembrance of Black men and women who died recently at the hands of police.
The national strike will also include a handful of worker-led marches through participating cities, organizers said Wednesday.
According to details shared exclusively with The Associated Press, organizers are demanding sweeping action by corporations and government to confront systemic racism in an economy that chokes off economic mobility and career opportunities for many Black and Hispanic workers, who make up a disproportionate number of those earning less than a living wage.
They also stress the need for guaranteed sick pay, affordable health care coverage and better safety measures for low-wage workers who never had the option of working from home during the coronavirus pandemic.
“We have to link these fights in a new and deeper way than ever before,” said Mary Kay Henry, president of the Service Employees International Union, which represents over 2 million workers in the US and Canada.
“Our members have been on a journey … to understanding why we cannot win economic justice without racial justice. This strike for Black lives is a way to take our members’ understanding about that into the streets,” Henry told the AP.
Among the strikers’ specific demands are that corporations and government declare unequivocally that “Black lives matter.” Elected officials at every level must use executive and legislative power to pass laws that guarantee people of all races can thrive, according to a list of demands. Employers must also raise wages and allow workers to unionize to negotiate better health care, sick leave and child care support.
The service workers union has partnered with the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, the American Federation of Teachers, United Farm Workers and the Fight for $15 and a Union, which was launched in 2012 by American fast food workers to push for a higher minimum wage.
Social and racial justice groups taking part include March On, the Center for Popular Democracy, the National Domestic Workers Alliance and the Movement for Black Lives, a coalition of over 150 organizations that make up the Black Lives Matter movement.
Ash-Lee Woodard Henderson, a strike organizer with the Movement for Black Lives, said corporate giants that have come out in support of the BLM movement amid nationwide protests over police brutality have also profited from racial injustice and inequity.
“They claim to support Black lives, but their business model functions by exploiting Black labor — passing off pennies as ‘living wages’ and pretending to be shocked when Covid-19 sickens those Black people who make up their essential workers,” said Henderson, co-executive director of Tennessee-based Highlander Research and Education Center.
“Corporate power is a threat to racial justice, and the only way to usher in a new economy is by tackling those forces that aren’t fully committed to dismantling racism,” she said in a statement Trece Andrews, a Black nursing home worker for a Ciena Healthcare-managed retirement home in the Detroit area, said she feels dejected after years of being passed over for promotions.
The 49-year-old believes racial discrimination plays a part in her career stagnation.
“I’ve got 20 years in the game and I’m only at $15.81 (per hour),” she said in a phone interview.
As the single mother of a 13-year-old daughter and caregiver to her father, a cancer survivor, Andrews said inadequate personal protective gear makes her afraid of bringing the coronavirus home from her job.
“We’ve got the coronavirus going on, plus we’ve got this thing with racism going on,” Andrews said.
“They’re tied together, like some type of segregation, like we didn’t have our ancestors and Martin Luther King fighting against these types of things. It’s still alive out here, and it’s time for somebody to be held accountable. It’s time to take action.” The strike continues a decades-old labor rights movement tradition. Most notably, organizers have drawn inspiration from the Memphis sanitation workers’ strike over low wages, benefits disparity between Black and white employees, and inhumane working conditions that contributed to the deaths of two Black workers in 1968.
At the end of that two-month strike, some 1,300 mostly Black sanitation workers bargained collectively for better wages.
“Strike for Black Lives” organizers say they want to disrupt a multi-generational cycle of poverty perpetuated by anti-union and other policies that make it difficult to bargain collectively for better wages and working conditions.
Systemic poverty affects 140 million people in the U.S, with 62 million people working for less than a living wage, according to the Poor People’s Campaign: A National Call for Moral Revival, a strike partnering organization.